Abstract
At the core of the therapeutic effect of HLA-matched allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) is T cell alloreactivity against minor histocompatibility antigens (mHAgs), polymorphic peptides resulting from donor-recipient disparity at sites of single nucleotide gene polymorphisms (SNPs). Despite their crucial role in graft-versus-leukemia (GvL) and graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), only few mHAgs have been characterized to date.
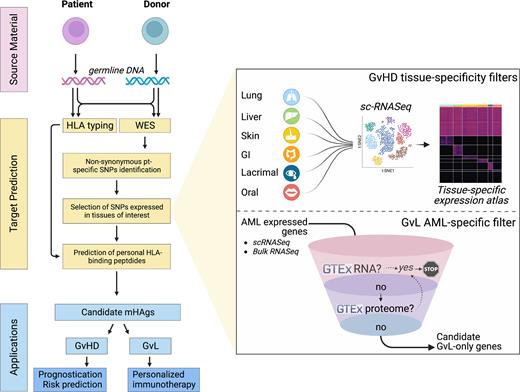
To systematically identify autosomal and Y-chromosome encoded HLA-I restricted mHAgs, we devised a computational pipeline based on: (i) comparison of whole exomes (WES) from paired donor-recipient DNA to define recipient-restricted exonic non-synonymous polymorphisms; and (ii) generation of expression filters by incorporating published single cell expression profiles from normal and malignant hematopoietic cells and GvHD target organs. For each GvHD tissue (skin, liver, GI, lung, oral mucosa and lacrimal gland), a large single cell database combining ≥1 independent datasets was created to cluster and annotate tissue-resident cell types. Cell-type specific genes were defined based on their total number of reads (CPM>5 in any cluster), thus creating an expression atlas capturing less frequent albeit biologically relevant cell types underestimated in bulk expression profiles. For GvL predictions, we built an AML-specific filter by defining AML-expressed genes from single cell and bulk data, and by subtracting genes with expression in non-hemopoietic tissues, per transcriptome and proteome GTEx databases. Candidate GvL/GvHD mHAgs prediction was performed by applying the HLAthena binding prediction tool on recipient-restricted SNPs expressed in GvL or GvHD tissues.
To validate the pipeline predictive power, we used a panel of 95 HLA class I monoallelic lines generated from B721.221 cells, which we previously profiled by WES, RNASeq and immunopeptidomics. By assigning the B721.221 genome as surrogate 'HCT recipient’ and the reference hg19 genome as surrogate 'donor', we identified recipient-restricted SNPs, whose class I-restricted presentation we confirmed by mass spectrometry for a median of 5 (range 1-16) predicted epitopes/ allele. For 2 HLA-A0201 epitopes encompassing SNPs with an allelic frequency <0.001, we validated immunogenicity through stimulation of PBMCs from HLA-A0201 healthy donors (HDs) with corresponding synthetic peptides. For Y-encoded mHAgs, we predicted a median of 62 (range 24-107) epitopes/HLA-I allele from 9 genes expressed (>1 TPM) in ≥1 non germline tissue. Analysis of 12 male immunopeptidomes confirmed presentation of 3 known Y mHAgs and 26 novel predicted epitopes across 18 alleles. To estimate the fraction of immunogenic predicted binders, we tested all Y epitopes predicted across 3 common alleles (A0201, B1801, C0501). Of 215 Y peptides tested, 53 (~25%) elicited an antigen-specific T cell response in PBMCs from female HDs, as per dextramer-based detection of ≥0.2% CD8 cells.
To test the prognostic potential of the mHAg load on cGvHD risk, we performed WES on 220 donor-recipient pairs treated with matched-related-donor allo-HCT for myeloid disease at DFCI between 2013-2020. Our logistic regression analysis used organ-specific NIH moderate/severe cGvHD as outcome; as covariates, we included tissue-specific mHAg load and standard HCT variables (disease type and prognostic risk, conditioning intensity, graft type, GvHD prophylaxis, female into male [F→M] transplant, relapse). The burden of lung-expressed mHAgs was correlated with lung GvHD occurrence (P=0.023). Liver GvHD was associated with F→M transplants (P=0.023). Subgroup analysis further showed liver GvHD to be correlated with the number of epitopes predicted from the RPS14Y gene (P=0.037).
For identification of AML-specific mHAgs, a median of 31 (range 13-50) mHAgs/patient were predicted in our cohort from 269 genes preferentially expressed in AML, with a trend for a protective effect of their load against relapse (P=0.058). Of note, 39 SNPs generated putative mHAgs shared by >10 patients and covering 8 common HLA-I alleles in Caucasians, thereby representing potential targets for post-HCT immunotherapy.
Overall, we report the generation of a robust analytic pipeline which enables the broadening of the repertoire of mHAgs available for donor selection and for predicting, monitoring or manipulating GvL and GvHD after allo-HCT.
Disclosures
Klaeger:Genentech, Inc.: Current Employment. Braun:Bristol Myers Squibb: Other: non financial support; LM Education/Exchange Services: Honoraria. Livak:Standard BioTools Inc.: Current equity holder in private company. Ho:Omeros: Consultancy; Allovir: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy; Jazz: Research Funding. Ritz:Equillium: Research Funding; Gadeta: Research Funding; Kite/Gilead: Research Funding; Oncternal: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Akron Biotech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AvroBio: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Clade Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Draper: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Garuda Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; LifeVault Bio: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Smart Immune: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Talaris Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TScan Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Soiffer:Gilead: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy; Rheos Therapeutics: Consultancy; VOR Biopharma: Consultancy; Juno: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Alexion: Consultancy; Be The Match/National Marrow Donor Program: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kiadis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Keskin:Affimed NV: Current equity holder in private company; Agenus Bio: Current equity holder in private company; Armata Pharmaceuticals: Current equity holder in private company; Breakbio: Current equity holder in private company; BioMarin Pharmaceutical: Current equity holder in private company; Celldex Therapeutics: Current equity holder in private company; Clovis Oncology: Current equity holder in private company; Editas Medicine: Current equity holder in private company; Exelixis: Current equity holder in private company; Gilead Sciences: Current equity holder in private company; Immunitybio: Current equity holder in private company; ImmunoGen: Current equity holder in private company; IMV: Current equity holder in private company; Lexicon Pharmaceuticals: Current equity holder in private company; Moderna: Current equity holder in private company; Neoleukin Therapeutics: Current equity holder in private company; Regeneron Pharmaceuticals: Current equity holder in private company. Getz:Scorpion Therapeutics: Consultancy, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Other: Founder; MSMutSig: Patents & Royalties; IBM: Research Funding; SignatureAnalyzer-GPU: Patents & Royalties; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; MSMuTect: Patents & Royalties; MSIDetect: Patents & Royalties; POLYSOLVER: Patents & Royalties. Wu:BioNTech: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal